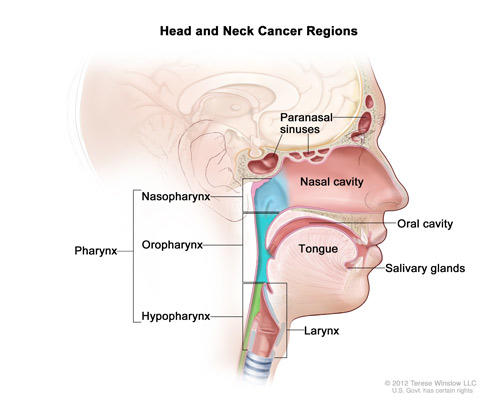
Head and neck cancer refers to a group of cancers that can develop in the head and neck region, including the mouth, throat, larynx (voice box), sinuses, and salivary glands. These cancers are often grouped together because they share similar risk factors and treatment approaches.
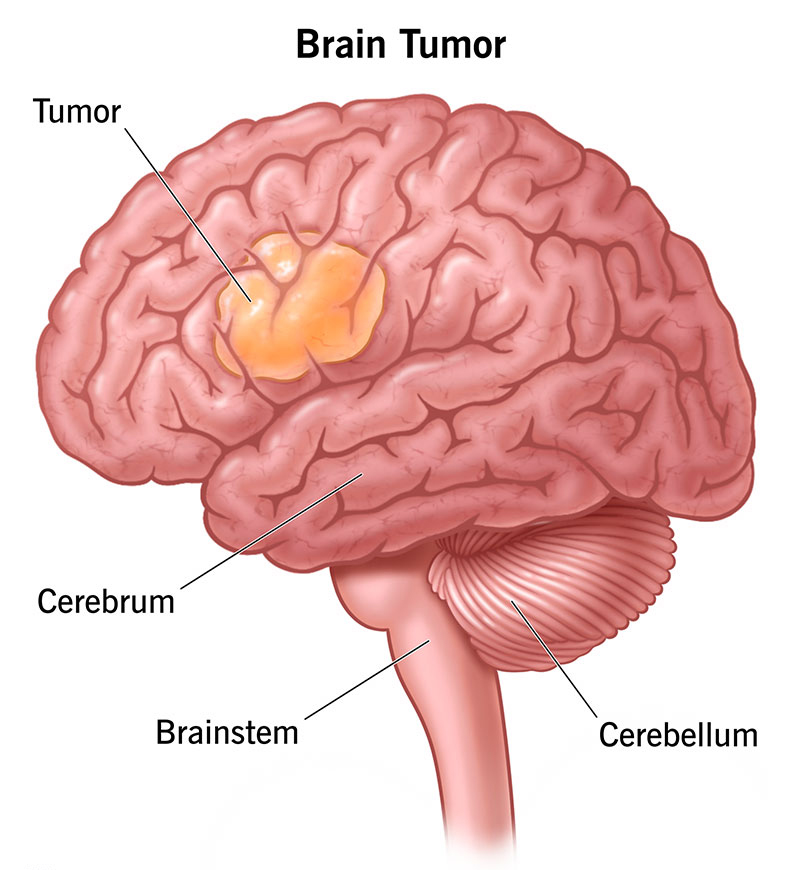
Brain tumors are abnormal growths of cells in the brain, and they can be either benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous). They can develop in different parts of the brain and vary in size, type, and behavior. Some brain tumors grow slowly, while others can spread aggressively.
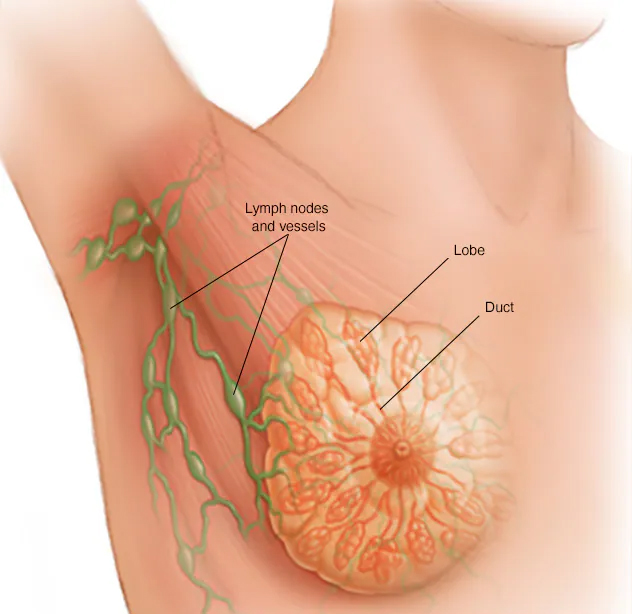
Breast cancer is one of the most common cancers, and it occurs when cells in the breast begin to grow uncontrollably. It can develop in both women and men, though it's far more common in women. There are different types of breast cancer, and it can vary greatly in terms of aggressiveness, symptoms, and treatment.
Ductal Carcinoma in Situ (DCIS) – A non-invasive form of breast cancer where abnormal cells are confined to the ducts and have not spread into surrounding tissues.
Invasive Ductal Carcinoma (IDC) – The most common type of breast cancer. It starts in the milk ducts and then spreads to nearby tissue.
Invasive Lobular Carcinoma (ILC) – Starts in the lobules (milk-producing glands) and then spreads to nearby tissue.
Inflammatory Breast Cancer – A rare and aggressive form where the breast becomes red, swollen, and warm due to the cancer blocking lymph vessels in the skin.
Triple-Negative Breast Cancer – A type of breast cancer that doesn't have estrogen receptors, progesterone receptors, or HER2 receptors. It's often more aggressive and harder to treat.
HER2-positive Breast Cancer – This type has higher than normal levels of HER2 (a protein that promotes cancer cell growth), which tends to make the cancer grow and spread more quickly.